





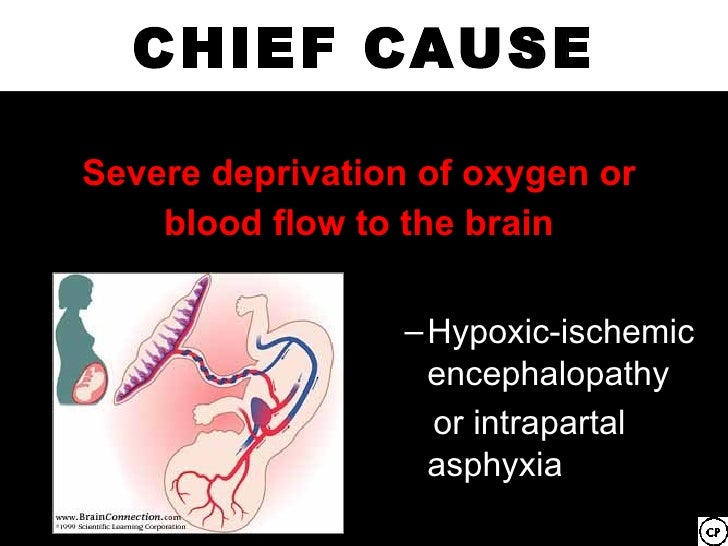









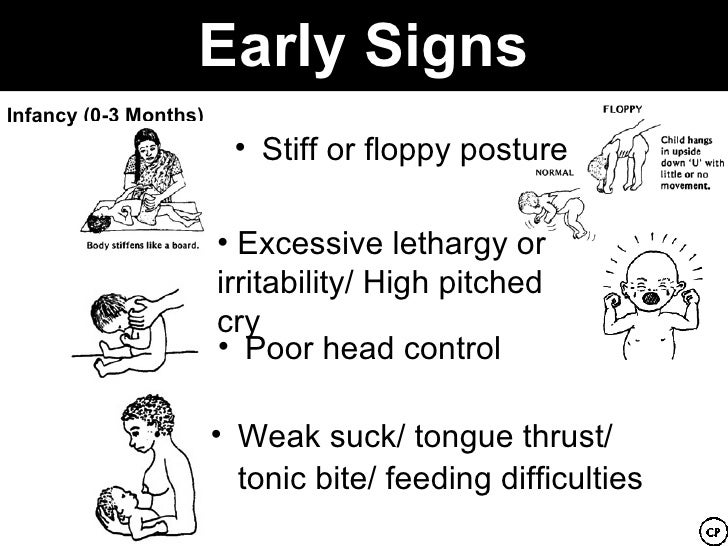






























**********************************************************************************



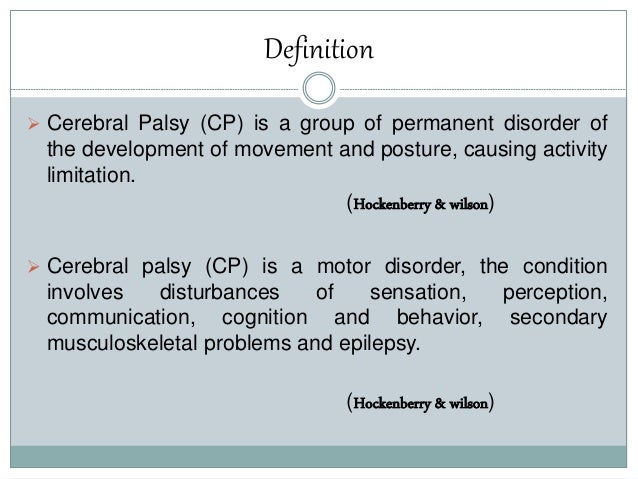








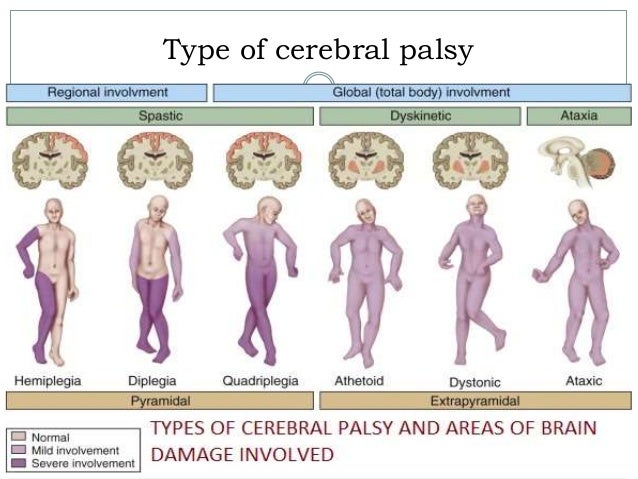






























*********************************************************************************************



PEDIATRICS – Study Material















































**********************************************************************************











































*********************************************************************************************


