
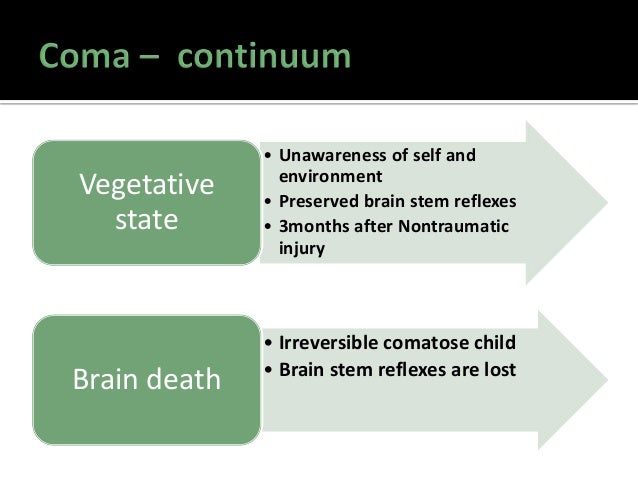
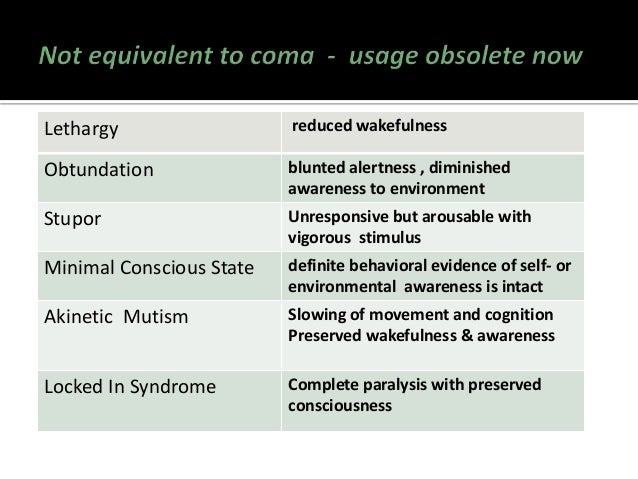































***********************************************************************








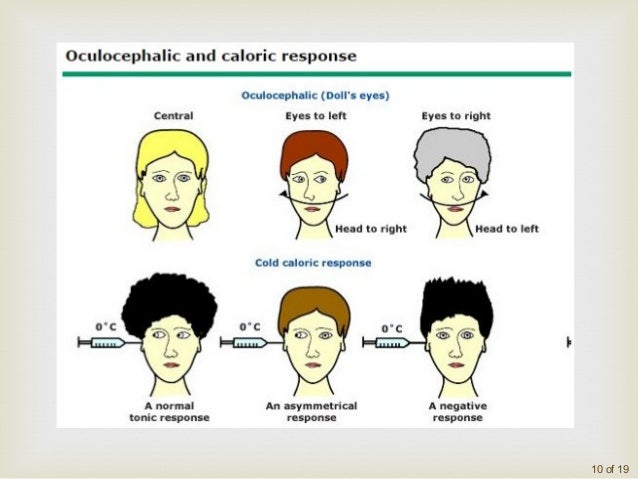
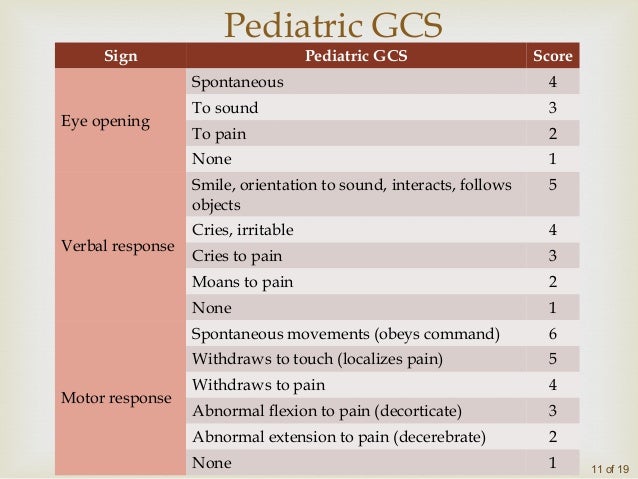




















































***************************************************************************














PEDIATRICS – Study Material


































***********************************************************************




































































***************************************************************************













