



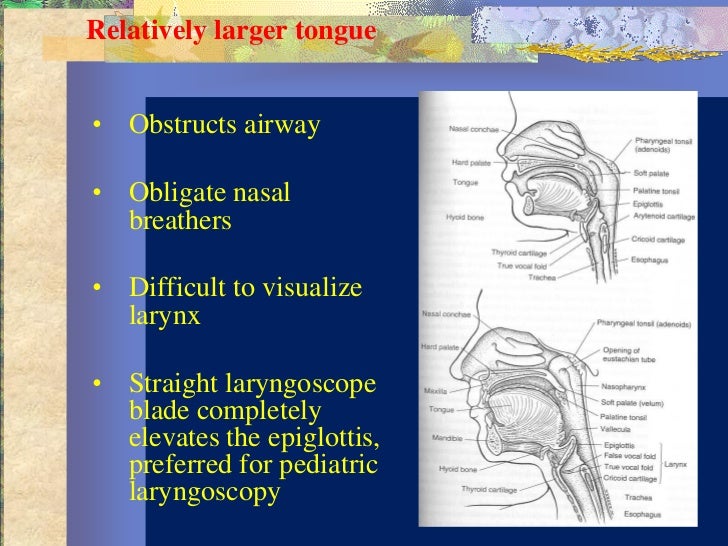









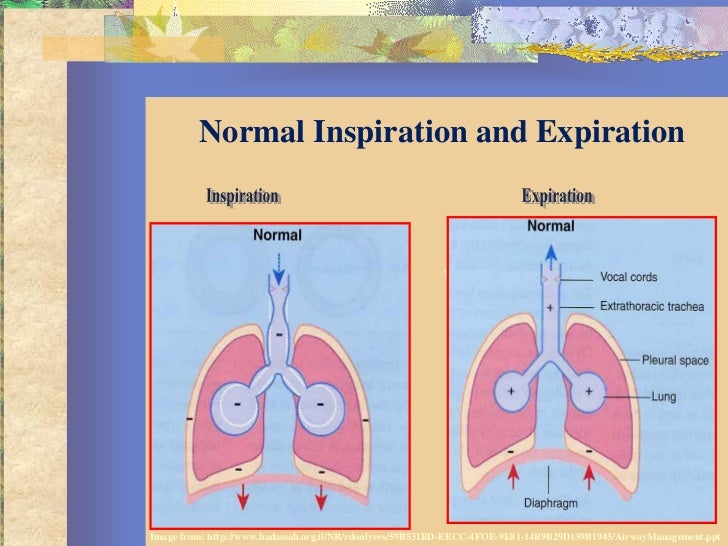












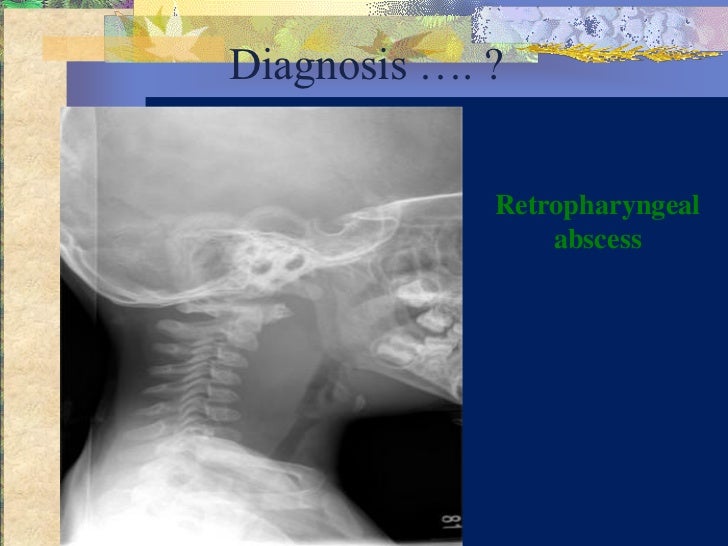
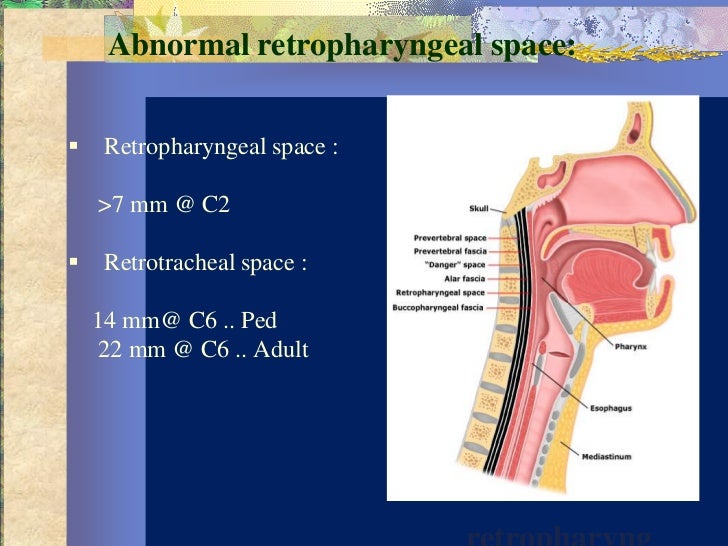












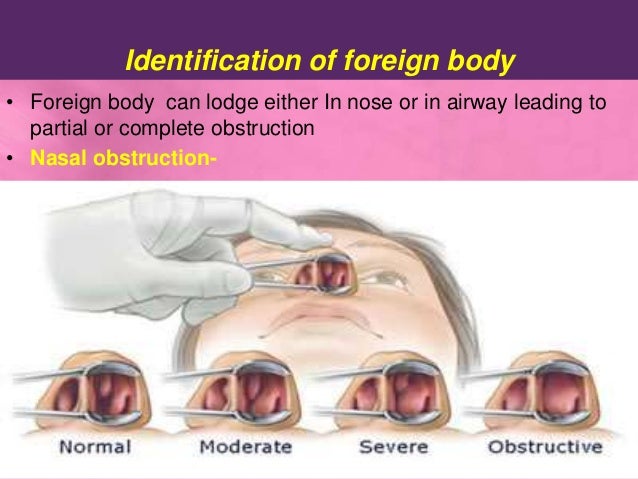
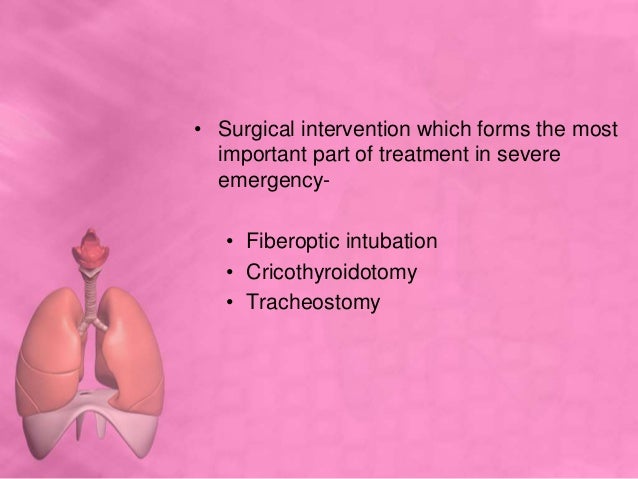
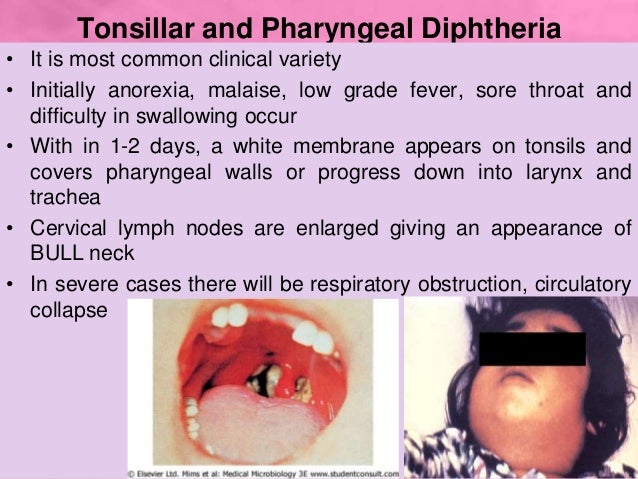
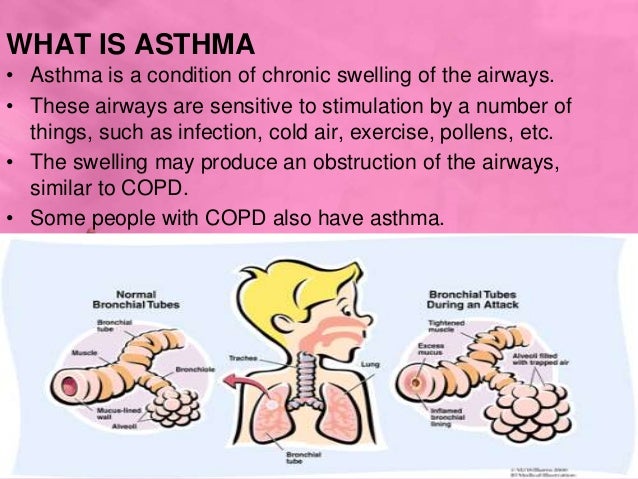
***************************************************************




































































***************************************************************






















































































PEDIATRICS – Study Material









































***************************************************************












































































***************************************************************





















































































