Classification of newborns & gestational age assessmen
What is a gestational age assessment?
Gestational age assessment means figuring out the number of weeks of your pregnancy. A full-term pregnancy is usually 40 weeks. It is important to assess if gestational age is uncertain or if your baby is smaller or larger than expected.
The new Ballard score is commonly used to determine gestational age. Here’s how it works:
-
Scores are given for 6 physical and 6 nerve and muscle development (neuromuscular) signs of maturity. The scores for each may range from -1 to 5.
-
The scores are added together to determine the baby’s gestational age. The total score may range from -10 to 50.
-
Premature babies have low scores. Babies born late have high scores.
How is physical maturity assessed?
The physical assessment includes an exam of the following physical characteristics:
-
Skin texture. Skin may be sticky, smooth, or peeling.
-
Lanugo. This is the soft downy hair on a baby’s body. It is absent in premature babies. It is present in full-term babies, but not in babies born late.
-
Plantar creases. These are the creases on the soles of the feet. They range from absent to covering the entire foot.
-
Breast. The thickness and size of the breast tissue and the areola (the darkened area around each nipple) are assessed.
-
Eyes and ears. Eyelids are checked to see if they are open or fused shut (more likely in a premature baby). The amount of cartilage and stiffness of the ear tissue are also noted.
-
Male genitals. The presence of testes and the look of the scrotum, from smooth to wrinkled, is verified.
-
Female genitals. The appearance and size of the clitoris and the labia are noted.
How is neuromuscular maturity assessed?
The neuromuscular assessment includes an exam of the following:
-
Posture. How the baby holds his or her arms and legs.
-
Square window. How far the baby’s hands can be flexed toward the wrist.
-
Arm recoil. How well the baby’s arms spring back to a flexed position.
-
Popliteal angle. How well the baby’s knees bend and straighten.
-
Scarf sign. How far the elbows can be moved across the baby’s chest.
-
Heel to ear. How close the baby’s feet can be moved to the ears.
Gestational age assessment is an important way to learn about your baby’s well-being at birth. By identifying any problems, your baby’s healthcare provider can plan the best possible care.
****************************************************************************
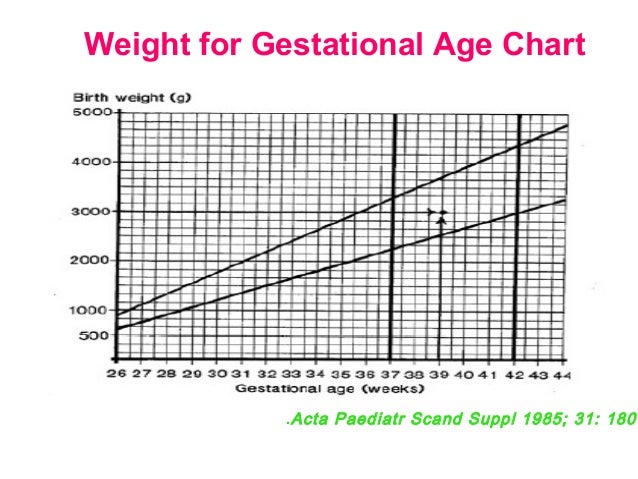
Gestational age and growth parameters help identify the risk of neonatal pathology. Gestational age is the primary determinant of organ maturity.
Gestational age is the time elapsed since the beginning of the woman’s last menstrual period; it is usually counted in weeks and days. Gestational age is not the actual embryologic age of the fetus.
Embryologic age is the time elapsed since the date of conception. By convention (and assuming a 28-day menstrual cycle), the embryologic age is 2 wk less than the gestational age. Women may more accurately estimate the date of conception based on their time of ovulation as identified by in-home hormonal testing and/or basal body temperature measurements.
However, the date of conception is definitively known only when in vitro fertilization or other assisted reproductive techniques are used because these techniques establish the date of conception.
Estimations of gestational age can be based on
The estimated date of confinement (EDC) is the date birth is expected (the due date). The EDC can be calculated as
When periods are regular and recorded contemporaneously, the menstrual history is relatively reliable.
Ultrasonographic measurements of the fetus in the 1st trimester give the most accurate estimate of embryologic age. When menstrual cycles are irregular or data are unreliable or not available, ultrasonography may be the sole source of the EDC. If the EDC estimated by dates differs from the EDC estimated by ultrasonography, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends (see Methods for Estimating Due Date) using the ultrasonographic date if it differs from the calculated date by
Because ultrasonographic estimates are less accurate later in pregnancy, 2nd and 3rd trimester ultrasonographic results should rarely be used to revise those done during the 1st trimester.
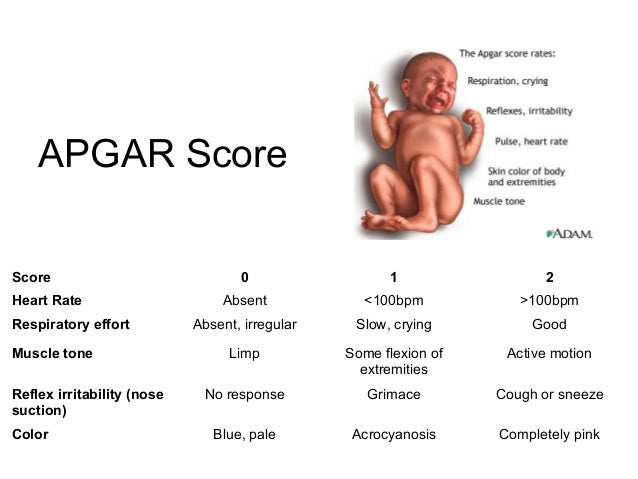
Newborn physical examination findings also allow clinicians to estimate gestational age using the new Ballard score. The Ballard score is based on the neonate’s physical and neuromuscular maturity and can be used up to 4 days after birth (in practice, the Ballard score is usually used in the first 24 h).
The neuromuscular components are more consistent over time because the physical components mature quickly after birth. However, the neuromuscular components can be affected by illness and drugs (eg, magnesium sulfate given during labor). Because the Ballard score is accurate only within plus or minus 2 wk, it should be used to assign gestational age only when there is no reliable obstetrical information about the EDC or there is a major discrepancy between the obstetrically defined gestational age and the findings on physical examination.
Assessment of gestational age—new Ballard score.
Based on gestational age, each neonate is classified as
-
Premature: < 34 wk gestation
-
Late pre-term: 34 to < 37 wk
-
Early term: 37 0/7 wk through 38 6/7 wk
-
Full term: 39 0/7 wk through 40 6/7 wk
-
Late term: 41 0/7 wk through 41 6/7 wk
-
Postterm: 42 0/7 wk and beyond
-
Postmature: > 42 wk
**************************************************************